This is a newsletter I create and share with my internal security team. Feel free to grab and do the same.
Sneaky2FA Phishing Kit Now Uses Browser-in-the-Browser to Steal Sessions
A recent update to the Sneaky2FA phishing-as-a-service toolkit adds a Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) fake login window, allowing attackers to harvest both credentials and active session tokens. This setup mimics a legitimate Microsoft login flow, making it difficult for users to spot the deception and enabling attackers to bypass MFA protections.
Key Insights
The phishing flow starts with a bot-protection challenge before displaying a fake Microsoft sign-in page.
Clicking “Sign in” triggers a fake pop-up window that resembles a real browser login prompt.
Attackers capture both credentials and session tokens, enabling full account takeover even when MFA is enabled.
The kit uses obfuscation, domain rotation, and conditional content loading to avoid automated detection.
Further Reading: Push Security
Fake CAPTCHA Triggers 42-Day Ransomware Chain (Unit 42 / Akira ransomware)
Unit 42 analyzed an incident where an employee clicked a fake CAPTCHA checkbox that served as a social-engineering lure. The interaction executed a malicious script that installed a remote-access Trojan, giving attackers an initial foothold. Over the next 42 days, the threat actors escalated privileges, moved laterally, exfiltrated nearly 1 TB of data, deleted backups, and ultimately deployed Akira ransomware — all without being detected until the final stages of the breach.
Key Insights
Fake CAPTCHA and human-verification prompts remain highly effective for initiating malware execution.
Security tooling may log malicious behavior without generating alerts if detection logic is misconfigured.
Once inside, attackers can use common administrative protocols to pivot, compromise privileged accounts, and deploy ransomware.
Weak segmentation, poor credential hygiene, and ineffective alerting significantly expand the blast radius of an initial compromise.
Further Reading: Unit 42
Fake “Calendly” Invites Used to Spoof Major Brands and Hijack Ad Manager Accounts
A phishing campaign is impersonating well-known brands by sending fake Calendly-style meeting invites designed to harvest credentials. The invites lead users to a fraudulent scheduling page, followed by a CAPTCHA and a spoofed login prompt. Attackers target users with access to Google Workspace, Facebook Business, and other advertising platforms, aiming to steal credentials or session tokens and take over ad-manager accounts.
Key Insights
Attackers are weaponizing familiar scheduling tools and trusted brand names to increase credibility.
Fake meeting invites tied to business outreach or job opportunities are being used as lures.
CAPTCHA steps and attacker-in-the-middle techniques help bypass two-factor authentication.
Compromised ad accounts can be abused for unauthorized spending, malvertising, or resale.
Further Reading: BleepingComputer
The Cloudflare Outage May Be a Security Roadmap (Krebs on Security)
A recent Cloudflare outage briefly took major websites and services offline after an internal configuration error disrupted core proxy functions. The event underscored how heavily organizations rely on Cloudflare for bot filtering, traffic routing, and web application protections — and how quickly those defenses can disappear when a single provider experiences a failure.
Key Insights
The outage was triggered by a database permission change that produced a malformed feature file, breaking Cloudflare’s bot-management system.
Organizations lost key protections such as bot mitigation and traffic filtering during the disruption.
Many customers scrambled to reroute DNS or bypass Cloudflare entirely, revealing that fallback plans were often untested.
The incident highlights concentration risk created by dependence on large cloud and CDN providers.
Further Reading: Krebs on Security
PowerShell 5.1 Now Warns Before Executing Scripts from Web Content
Microsoft has updated Windows PowerShell 5.1 so that running Invoke-WebRequest (including the curl alias) against a webpage now triggers a security confirmation prompt. The prompt warns that embedded scripts in the retrieved content could run if processed using the legacy HTML parser. Users must choose to proceed or cancel, and declining halts the action. Using the -UseBasicParsing parameter avoids script execution entirely and prevents the prompt, making it the safer option for automation.
Key Insights
A new confirmation prompt appears when fetching web content that might contain executable scripts.
The -UseBasicParsing parameter avoids script execution and prevents the prompt from interrupting automated workflows.
Legacy HTML parsing now requires explicit user approval when running interactively.
The update reduces the chance of unintentionally executing malicious code embedded in fetched web content.
Further Reading: Microsoft Support
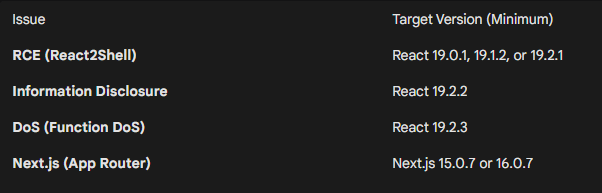
Critical React2Shell Vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) Exploited in the Wild (Bitdefender)
The critical vulnerability CVE-2025-55182, known as React2Shell, affects React Server Components and frameworks like Next.js. The issue stems from unsafe deserialization in how server-side component payloads are handled, allowing unauthenticated remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands. Since disclosure, exploitation has accelerated, with botnets and automated scanners actively targeting both consumer smart-home infrastructure and cloud-hosted web applications.
Key Insights
The flaw enables unauthenticated remote code execution through crafted requests to vulnerable endpoints.
Attackers have rapidly integrated the exploit into automated campaigns and botnet activity.
React Server Components and major frameworks built on them are widely affected, increasing exposure across modern web stacks.
Observed exploitation often deploys cryptominers, backdoors, or additional post-exploitation tools.
Further Reading: Bitdefender
ConsentFix: Browser-Native OAuth Consent Hijacking
A newly identified phishing technique called ConsentFix combines ClickFix-style interaction tricks with OAuth consent abuse. Attackers direct victims to compromised, high-reputation sites where fake verification prompts are shown. Victims are manipulated into completing a legitimate OAuth authorization flow and then pasting the resulting authorization code into the attacker-controlled page. This grants persistent account access without stealing passwords or bypassing MFA, because the attacker leverages legitimate OAuth mechanisms used by trusted applications such as Azure CLI.
Key Insights
ConsentFix operates entirely within the browser, preventing endpoint security tools from detecting the takeover step.
Victims can be compromised even while already signed in, with no credential or MFA submission required.
The technique abuses inherently trusted OAuth flows from first-party applications.
Delivery via search-engine results and compromised sites bypasses email-focused phishing defenses.
Conditional loading and other evasion tactics make detection significantly harder.
Further Reading: Push Security
OWASP Releases Top 10 Risks and Mitigations for Agentic AI Security (PR Newswire)
The OWASP GenAI Security Project has released its Top 10 for Agentic Applications, a peer-reviewed framework outlining the most critical security risks associated with autonomous and agent-driven AI systems. Developed through more than a year of collaboration with over 100 experts, the list highlights how agentic AI introduces new categories of threats that don’t align with traditional software-vulnerability models, emphasizing risks that emerge when AI systems plan, decide, and act independently.
Key Insights
The Top 10 framework identifies high-impact risk categories such as goal hijacking, privilege misuse, and uncontrolled execution of tools.
Many agentic risks appear early in the workflow, particularly as agents start taking autonomous actions.
The project includes threat models and mitigation strategies to help organizations secure agent-powered systems.
Broad industry participation demonstrates growing urgency around securing agentic AI before widespread adoption.
Further Reading: PR Newswire
Microsoft Teams to Warn of Suspicious External Domain Traffic
Microsoft is introducing an External Domains Anomalies Report for Teams to help administrators detect unusual or risky interactions with external domains. The feature monitors messaging trends — including sudden spikes in traffic, new external domains, or abnormal engagement patterns — to flag potential security threats related to cross-organization communication. This gives IT teams better visibility into external collaboration and can help identify compromised accounts or risky data-sharing behaviors before they escalate.
Key Insights
The report identifies anomalies in message volume and interactions with external domains that may indicate compromised accounts or malicious activity.
Administrators can use the insights to distinguish between legitimate business communication and potential threats.
This feature complements other Teams security enhancements, such as warnings for malicious links and protections against unsafe content.
The rollout is planned globally in early 2026, allowing organizations to prepare for adoption.
Further Reading: Cybersecurity News
Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) Phishing Targeting Microsoft 365 and Okta (Datadog Security Labs)
An active AiTM phishing campaign is targeting organizations that use Microsoft 365 and Okta for single sign-on. The attackers proxy legitimate authentication flows through convincing lookalike pages, preserving branding while intercepting credentials and session cookies. The campaign adapts dynamically, detecting federated environments and redirecting victims to tailored login flows to maximize session hijacking success.
Key Insights
The phishing infrastructure closely mirrors legitimate Microsoft 365 and Okta SSO workflows, increasing user trust.
Client-side scripts are injected to capture credentials and session cookies in real time.
Lookalike domains and anti-automation controls are used to add legitimacy and evade analysis.
Email lures commonly reference employee benefits or compensation themes to prompt interaction.
By acting as a live proxy, the attack can bypass many MFA methods that are not phishing-resistant.
Further Reading: Datadog Security Labs
Access Granted: Phishing Abuse of Device Code Authorization
A new phishing trend is exploiting Device Code Authorization flows — a common method many services use to let users sign in on shared or secondary devices (like TVs) by entering a code shown elsewhere. Attackers are crafting phishing lures that direct victims to fake “authorization” pages where they’re prompted to enter a device code. Once entered, the code links the attacker’s session to the victim’s account, giving the attacker instant access without the victim ever entering credentials or MFA codes.
Key Insights
Attackers misuse legitimate device-code sign-in flows to take over accounts without stealing passwords.
Victims can inadvertently grant access simply by entering a displayed code on a malicious page.
Because no credentials are entered, many defenses (including MFA) don’t block this technique.
This method highlights the importance of educating users about out-of-band authentication flows and confirming unexpected prompts before entering codes.
Further Reading: Proofpoint
Cybercriminals Exploiting .onmicrosoft.com Domains to Launch TOAD Scam Attacks
Cybercriminals are abusing legitimate Microsoft tenant domains that end in “.onmicrosoft.com” to deliver TOAD (Telephone-Oriented Attack Delivery) scams. By sending messages from these trusted-looking domains, attackers can bypass security filters and convince recipients that the communication is associated with Microsoft. Victims are then prompted to call fraudulent support numbers, where they are manipulated into disclosing credentials or other sensitive information.
Key Insights
Default “.onmicrosoft.com” tenant domains are being used to make scam messages appear legitimate.
The trusted reputation of these domains helps attackers evade email and messaging security controls.
Victims are often directed to call fake support numbers rather than click links.
The activity demonstrates how legitimate cloud infrastructure can be repurposed to support social-engineering campaigns.
Further Reading: Cybersecurity News
Insider Threats: Hackers Paying Company Insiders to Bypass Security (Hackread)
Threat actors are increasingly turning to insider recruitment to bypass organizational security controls. Instead of exploiting vulnerabilities from the outside, criminal groups are offering employees direct payments in exchange for internal access, sensitive data, or assistance disabling safeguards. These efforts are commonly advertised through underground forums and private messaging channels and span multiple industries, including finance, technology, and cloud services.
Key Insights
Criminal groups are offering cash payments for insider assistance, often for one-time access or specific data.
Recruitment tactics may include appeals to financial stress or dissatisfaction with work.
Insider access can allow attackers to sidestep defenses such as MFA, logging, and monitoring tools.
The trend shows a shift toward human-based attack paths rather than purely technical exploitation.
Further Reading: Hackread
Calendar-Invite Phishing Campaigns Use Meeting Invites as Lures
Attackers are increasingly using fake calendar invitations as a phishing vector. These malicious invites may arrive by email or through synced calendar apps, often appearing to come from familiar contacts or trusted services. When a recipient interacts with the invite — for example, by clicking a link to join a “meeting” — they can be led to spoofed login pages designed to harvest credentials or other sensitive information. This technique leverages the trust people place in calendar events and routine scheduling workflows to bypass skepticism.
Key Insights
Malicious invites look like legitimate meeting requests: Attackers spoof sender names and use familiar branding to increase credibility.
Links in calendar events can lead to credential-harvesting sites: Clicking “Join” or related links may redirect users to phishing pages.
Attackers abuse calendar sync and notification features: Because events often appear automatically on connected devices, users may interact without verifying the source.
This technique blends social engineering with platform abuse: It takes advantage of the routine nature of scheduling to reduce suspicion.
Further Reading: HoxHunt
Google Malvertising Attack Uses Search Ads to Deliver Phishing and Malware
A recently analyzed campaign showed how attackers are abusing Google Search Ads to distribute malicious redirects and phishing lures. Instead of relying on compromised websites or email alone, the adversary purchased search ad placements that appeared for high-traffic queries. When users clicked these ads, they were taken through a chain of redirects and deceptive pages that ultimately led to credential-harvesting forms or malware delivery. Because the initial entry point came from legitimate ads, many victims didn’t suspect the content was malicious — and traditional web-filtering tools often trust paid search results by default.
Key Insights
Malicious actors are buying legitimate search ad placements for popular queries to maximize reach.
Clicking the ad triggers redirects and cloaked landing pages that conceal the malicious intent until the final stage.
Credential harvesting and malware downloads are delivered through deceptive page flows that mimic real services.
Because the initial interaction comes from an ad, users may trust the link more than typical phishing emails or unknown sites.
Further Reading: Push Security
BlackForce Phishing Kit Technical Analysis (Zscaler)
A recent technical analysis of the BlackForce phishing kit reveals it’s a highly customizable and modular phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) offering that enables attackers to rapidly deploy credential harvesting campaigns against a variety of targets. The kit supports multiple social-engineering motifs, dynamic content generation, and advanced obfuscation techniques, making it difficult for security tooling to detect at scale. BlackForce has been linked to campaigns that target enterprise single-sign-on portals, cloud services, and financial platforms by replicating legitimate login flows while capturing credentials and session tokens.
Key Insights
BlackForce is modular, allowing attackers to tailor templates to mimic specific services and bypass naive detection based on static indicators.
It uses dynamic content delivery and URL rotation to avoid pattern-based detection and evade automated scanners.
The kit captures not only user credentials but also session tokens, enabling broader account takeover when paired with weak or non-phishing-resistant MFA.
BlackForce campaigns often use additional obfuscation layers and intermediary redirects to hide phishing infrastructure and make takedown more difficult.
Because of its ease of deployment and adaptability, BlackForce has proliferated in underground markets, lowering the bar for threat actors to launch sophisticated phishing attacks.
Further Reading: Zscaler
Top Phishing Trends for 2025
Security researchers have identified several key phishing trends that defined 2025 — highlighting how attackers continue to evolve both their techniques and delivery mechanisms. These trends emphasize that phishing is no longer confined to simple email links, but increasingly combines social engineering with platform abuse, deceptive flows, and legitimate-looking vectors to bypass defenses and capture credentials, session tokens, and MFA responses.
Key Insights
Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) attacks remain prevalent, using fake pop-ups that mimic legitimate login dialogs to harvest credentials and active sessions.
Consent-based abuse techniques are growing, where attackers trick users into granting OAuth consent or other permissions that grant access without passwords.
Search-engine and ad-based delivery shows attackers buying and manipulating legitimate channels to increase reach and bypass filters.
Fake verification flows (CAPTCHAs, device codes, and human-verification prompts) continue to be effective in tricking users into executing commands or authorizing access.
AiTM and proxy-style phishing remains a persistent threat, capturing session tokens even when MFA is present.
Further Reading: Push Security
Access-Granted Phishing Abuse of Device Code Authorization (Proofpoint)
Threat actors are increasingly exploiting device code authorization flows — a method used by many online services to let users sign in on secondary or shared devices by entering a short code. In this abuse pattern, phishing lures direct victims to fake authorization pages where they’re prompted to enter a code. When the code is submitted, the attacker’s session becomes linked to the victim’s account, giving the attacker access without the victim ever entering credentials or MFA data.
Key Insights
Attackers misuse legitimate device-code sign-in flows to take over accounts without stealing passwords.
Victims can inadvertently grant access simply by entering a displayed code on a malicious page.
Because no credentials are entered, many defenses — including MFA — don’t block this technique.
This method highlights the need to educate users about out-of-band authentication prompts and to verify unexpected requests before entering codes.
Further Reading: Proofpoint
Phishing Campaign Abuses Google Cloud Automation to Evade Detection (Check Point)
Researchers have identified a phishing campaign that misuses legitimate Google Cloud automation features to distribute phishing emails at scale. By sending messages through trusted Google infrastructure, attackers make their lures appear authentic and bypass reputation-based email defenses. The emails mimic routine enterprise notifications and route victims through trusted cloud services before redirecting them to credential-harvesting pages.
Key Insights
Legitimate cloud automation capabilities are being repurposed to send phishing emails from trusted infrastructure.
Familiar enterprise notification themes are used to lower suspicion and encourage interaction.
Initial links often pass through trusted cloud services before redirecting to phishing pages.
The technique demonstrates how workflow and automation features can be abused to increase phishing success and evade detection.
Further Reading: Check Point
Malicious npm Packages Used as Phishing Infrastructure to Steal Credentials (The Hacker News)
Researchers uncovered a targeted campaign in which attackers published 27 malicious packages to the npm registry and abused the platform’s content-delivery infrastructure to host phishing pages. Rather than distributing malware through package installation, the attackers used npm-hosted resources to serve HTML and JavaScript lures that impersonated document-sharing portals and Microsoft sign-in flows. The campaign primarily targeted sales and commercial personnel across multiple industries.
Key Insights
Malicious npm packages were used as hosting infrastructure for phishing content rather than for delivering code via installation.
Phishing pages mimicked trusted services to capture user credentials.
Anti-analysis techniques such as bot filtering and obfuscated scripts were used to hinder detection.
Some infrastructure overlapped with adversary-in-the-middle phishing tooling.
The activity demonstrates how open-source ecosystems can be abused as resilient platforms for phishing operations.
Further Reading: The Hacker News
Shai-Hulud 3.0 Supply Chain Worm Emerges
Researchers have identified a new variant of the Shai-Hulud npm supply chain worm, commonly referred to as Shai-Hulud 3.0 or “The Golden Path.” This iteration builds on earlier versions by maintaining install-time execution within compromised packages while improving stealth, reliability, and compatibility across environments. Current observations suggest the activity may represent testing or refinement rather than a large-scale outbreak.
Key Insights
Shai-Hulud 3.0 continues the use of malicious install scripts that execute automatically during dependency installation.
The updated variant emphasizes improved error handling and cross-platform execution.
Credential harvesting from developer systems and CI/CD environments remains a core objective.
Indicators suggest the activity may be exploratory or preparatory ahead of a broader campaign.
Further Reading: Snyk
2025 CVE Data Review and Trends
A review of 2025 CVE data shows the highest volume of publicly disclosed vulnerabilities on record, with more than 48,000 CVEs published during the year. While overall severity distribution remained relatively consistent with prior years, the sheer scale of disclosures continues to complicate vulnerability management and prioritization efforts. The analysis also highlights how web application flaws and third-party ecosystems are driving much of the growth.
Key Insights
2025 set a new record for CVE disclosures, continuing a multi-year upward trend.
A large share of vulnerabilities fell into medium and high severity ranges, increasing triage pressure.
Web application issues such as cross-site scripting and injection remain the most common weakness classes.
Third-party and plugin ecosystems contributed significantly to overall CVE volume.
Disclosure activity showed uneven distribution throughout the year, with spikes tied to coordinated releases.
Further Reading: Jerry Gamblin